1. If you meant: “How do you treat a Varicella abscess?”
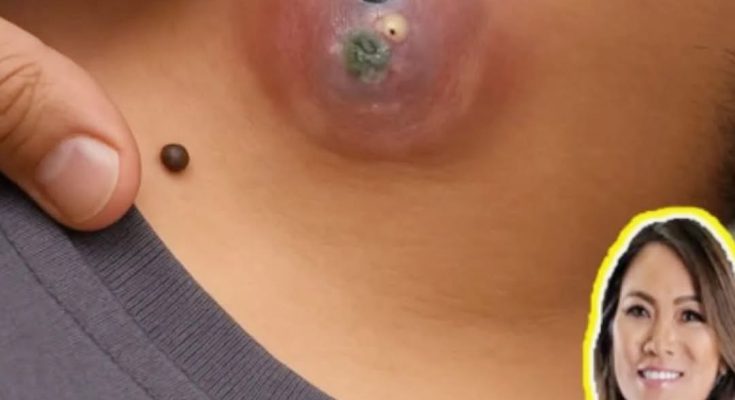
Varicella (chickenpox) is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, and secondary bacterial skin infections like abscesses can occur due to scratching the lesions.
✅ Management of a Varicella-Associated Abscess:
-
Identify the abscess: Usually localized swelling, redness, warmth, and pus.
-
Antibiotics:
-
Start empiric antibiotics covering Staphylococcus aureus (including MRSA in some areas) and Streptococcus pyogenes.
-
Examples: Clindamycin, Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (if MRSA suspected), or Cephalexin (if low MRSA risk).
-
-
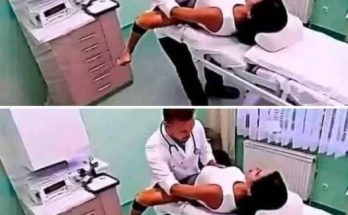
Incision and drainage (I&D):
-
If the abscess is large or fluctuant, I&D is the primary treatment.
-
-
Supportive care:
-
Continue antiviral treatment (e.g., acyclovir) if the varicella infection is still active or severe.
-
Pain management, hydration, and hygiene.
-
When to hospitalize:
-
Large or multiple abscesses
-
Systemic signs (fever, malaise)
-
Immunocompromised patients
-
Involvement of deeper tissues (cellulitis, necrotizing fasciitis)
2. If you meant: “How do you diagnose a Varicella abscess?”
Diagnosis is mainly clinical:
-
History of recent varicella infection (fever, itchy vesicular rash)
-
Appearance of red, tender, fluctuant areas (suggesting abscess)
-
May need ultrasound to confirm abscess vs. cellulitis
-
Culture of pus (if drained) helps guide antibiotic therapy